What is Multi-Task Learning?¶
Multi-Task Learning (MTL) is an active research field in machine learning. It is a learning paradigm which aims to jointly learn several related tasks to improve their generalization performance by leveraging common knowledge among them. In recent years, many researchers have successfully applied MTL to different fields such as computer vision, natural language processing, reinforcement learning, recommendation system and so on.
The recent studies of MTL mainly focus on two perspectives, network architecture design and loss weighting. We implement some general and representative methods in LibMTL.
For more relevant introduction, please refer to [1, 2, 3, 4].
Network Architecture¶
In the design of network architectures, the simplest and most popular method is the hard parameter sharing (HPS, LibMTL.architecture.HPS), as shown in Fig. 1, where an encoder is shared among all the tasks and each task has its own specific decoder. Since most of the parameters are shared among tasks, such architecture easily causes negative sharing when tasks are not related enough. To better deal with task relationships, different MTL architectures have been proposed. LibMTL supports several state-of-the-art architectures, please refer to LibMTL.architecture for details.
There are usually two types of MTL problems: the single-input problem and the multi-input problem. The single-input problem, as shown in the left of Fig. 1, means an input data has an output for each task or equivalently all tasks share the input data. The NYUv2 dataset is an example of this problem. The multi-input problem, as shown in the right of Fig. 1, indicates each task has its own input data. The Office-31 and Office-Home datasets belong to such problem. LibMTL has unified these two cases in a training framework and you just need to set the command-line argument multi_input correctly.
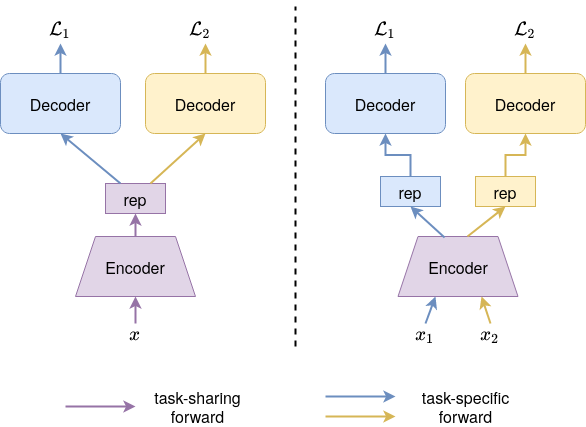
Fig. 1 An illustration of the single-input problem (left) and the multi-input problem (right), using hard parameter sharing pattern as an example.¶
Weighting Strategy¶
Balancing multiple losses corresponding to multiple tasks is another way to deal with task relationships since the shared parameters are updated by all the task losses. Thus, different methods have been proposed to balance losses or gradients. LibMTL supports several state-of-the-art weighting strategies, please see LibMTL.weighting for details.
Some gradient balancing methods such as MGDA (LibMTL.weighting.MGDA) need to compute the gradient for each task first and then calculate the aggregated gradient in various ways. To reduce the computational cost, it can use the gradients of the representations after the encoder (abbreviated as rep-grad) to approximate the gradients of shared parameters (abbreviated as param-grad).
The PyTorch implemention of rep-grad is shown in Fig. 2. We need to separate the computational graph into two parts by the detach operation. LibMTL has unified the two cases in a training framework and you just need to set the command-line argument rep_grad correctly. Besides, the argument rep_grad does not conflict with multi_input.
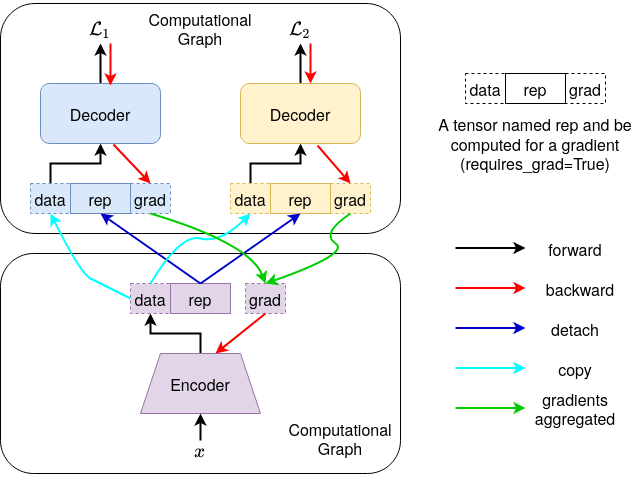
Fig. 2 An illustration of how to compute the gradient for representation.¶
References¶
- 1
Yu Zhang and Qiang Yang. A survey on multi-task learning. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2021.
- 2
Simon Vandenhende, Stamatios Georgoulis, Wouter Van Gansbeke, Marc Proesmans, Dengxin Dai, and Luc Van Gool. Multi-task learning for dense prediction tasks: a survey. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021.
- 3
Baijiong Lin, Feiyang Ye, and Yu Zhang. A closer look at loss weighting in multi-task learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2111.10603, 2021.
- 4
Michael Crawshaw. Multi-task learning with deep neural networks: a survey. arXiv preprint arXiv:2009.09796, 2020.